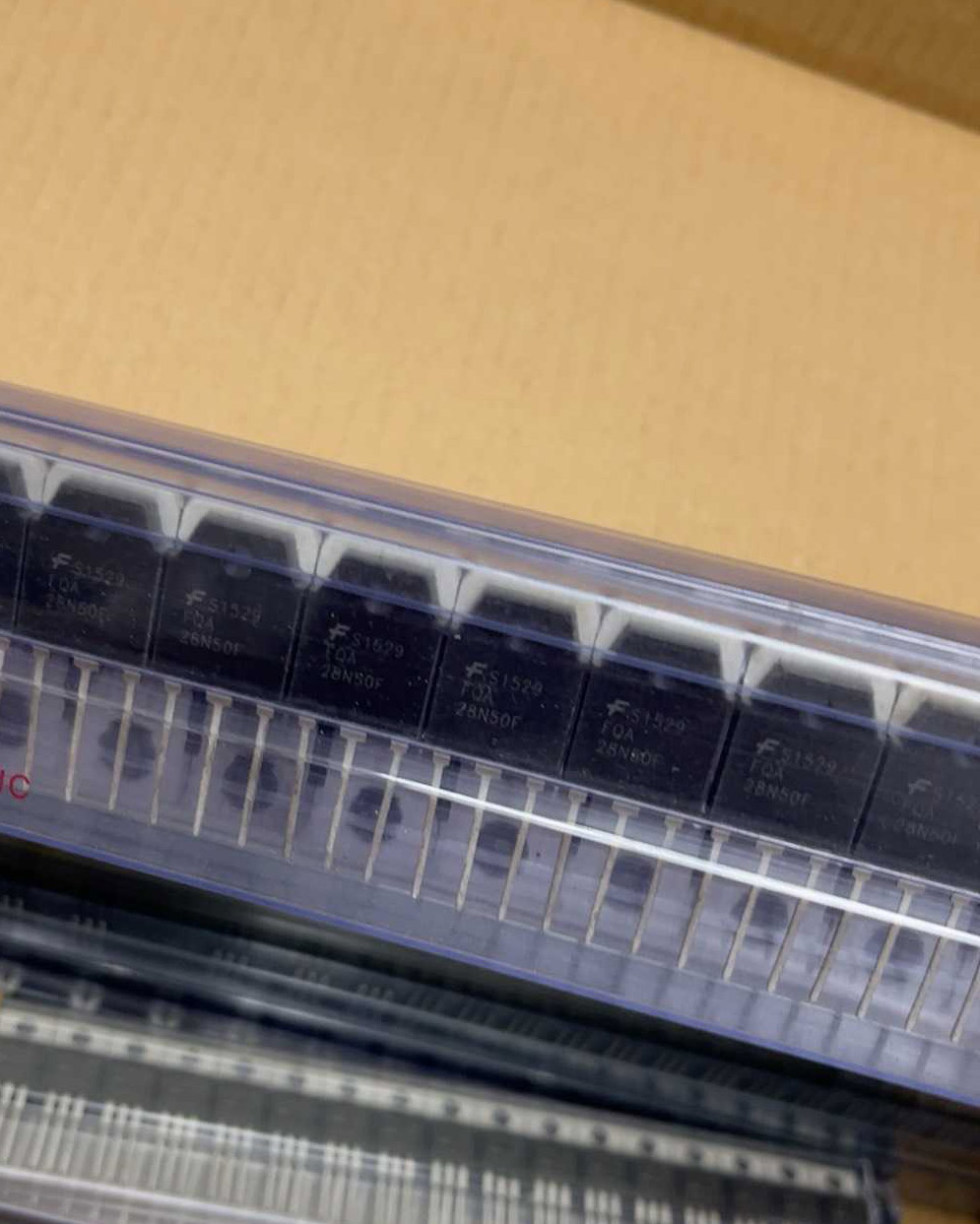
Function Description of FQA28N50F Chip
1. General Introduction
The FQA28N50F is a high – voltage, high – current N – channel power MOSFET (Metal – Oxide – Semiconductor Field – Effect Transistor) produced by well – known semiconductor manufacturers. It is designed to meet the requirements of various power – switching applications with excellent performance and reliability.
2. Electrical Characteristics and Basic Functions
2.1 Voltage and Current Ratings
- Drain – Source Voltage (VDS): The FQA28N50F can withstand a maximum drain – source voltage of 500V. This high – voltage rating makes it suitable for applications that involve high – voltage power supplies, such as switch – mode power supplies (SMPS), where the voltage levels can be relatively high during the switching process.
- Continuous Drain Current (ID): It can handle a continuous drain current of up to 28A at a specified temperature. This large current – carrying capacity enables it to drive high – power loads, such as motors in industrial or automotive applications, or high – power LED arrays in lighting systems.
2.2 Low On – Resistance
- The on – resistance (RDS(on)) of the FQA28N50F is relatively low. A low on – resistance is crucial as it reduces power losses in the MOSFET when it is in the on – state. When current flows through the MOSFET, the power dissipated as heat is proportional to the square of the current and the on – resistance (P = I²R). A lower RDS(on) means less heat generation, which improves the efficiency of the circuit and allows the MOSFET to operate at higher power levels without overheating. This is particularly important in high – power applications where energy efficiency is a key concern.
2.3 Fast Switching Speed
- The FQA28N50F features fast switching times, including turn – on and turn – off times. Fast switching speeds are essential for applications that require high – frequency operation, such as in high – frequency SMPS or in PWM (Pulse – Width Modulation) control circuits. In a PWM circuit, the MOSFET is rapidly switched on and off to control the average power delivered to a load. A fast – switching MOSFET can accurately follow the high – frequency PWM signals, enabling precise control of the power output.
3. Applications
3.1 Switch – Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
- In SMPS, the FQA28N50F is used as a switching element. It alternates between the on and off states at a high frequency to convert the input DC voltage to a high – frequency AC voltage, which is then rectified and filtered to obtain the desired output DC voltage. Its high – voltage rating allows it to handle the input voltage, and its low on – resistance and fast switching speed contribute to the high efficiency and high – frequency operation of the power supply.
3.2 Motor Control
- For motor control applications, the FQA28N50F can be used in H – bridge or half – bridge circuits to control the direction and speed of DC motors. By switching the MOSFETs in the circuit on and off in a specific sequence, the current flow through the motor can be controlled, enabling forward and reverse rotation and variable – speed operation. Its high – current – handling capacity makes it suitable for driving medium – to large – sized motors.
3.3 Lighting Systems
- In high – power LED lighting systems, the FQA28N50F can be used to control the power supply to the LEDs. PWM dimming techniques can be applied using the MOSFET to adjust the brightness of the LEDs. The fast switching speed of the MOSFET allows for smooth and efficient dimming control, and its low on – resistance helps to minimize power losses in the lighting circuit.
3.4 Inverters
- In inverters, which convert DC power to AC power, the FQA28N50F can be used as a key switching component. It switches the DC input voltage to generate an AC output voltage with the desired frequency and amplitude. The high – voltage and high – current capabilities of the MOSFET make it suitable for use in both small – scale and large – scale inverter applications, such as in solar power inverters or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS).
4. Protection Features
- Although the FQA28N50F itself may not have built – in comprehensive protection circuits, in practical applications, external protection circuits can be designed in conjunction with it. For example, over – current protection can be implemented using current – sensing resistors and protection chips to prevent excessive current from flowing through the MOSFET, which could damage it. Over – voltage protection can also be added to safeguard the MOSFET from voltage spikes and surges that may occur in the circuit. Additionally, proper heat – sinking design is necessary to ensure that the MOSFET operates within its safe operating temperature range, as excessive heat can degrade its performance and reliability.

















Leave a Reply